LANTIME: Configuring NTP Symmetric Key Authentication
These instructions describe how to prepare a LANTIME for NTP symmetric key authentication and explain how to configure the NTP client side, using the example of a Linux ntpd client. It's worth to mention that NTP clients which query the LANTIME without a key are still getting served with time, even if the LANTIME is prepared for symmetric key authentication. The feature is simply an additional security feature for those clients who want to use symmetric key authentication.
Configuration through the LANTIME WebUI
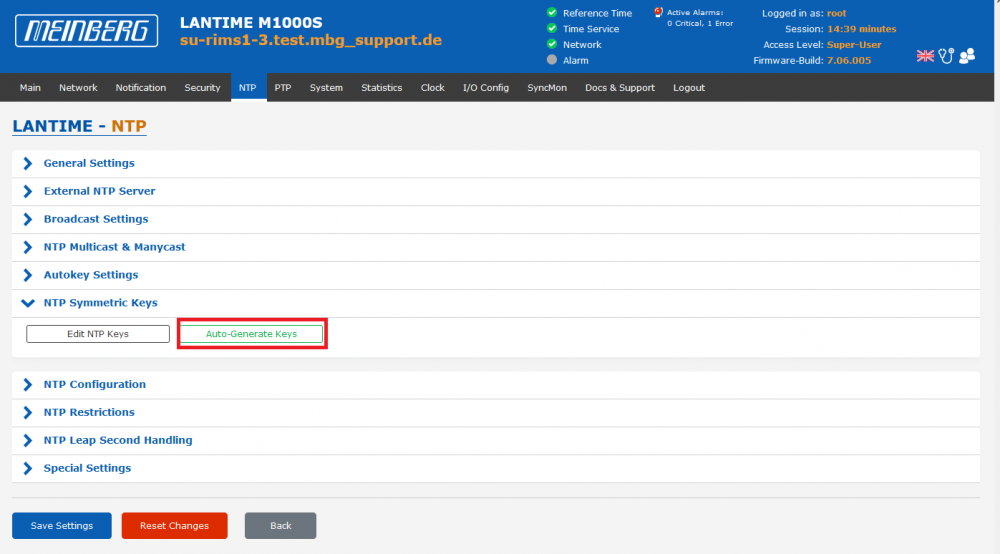
1. First, symmetric keys have to be generated. This can be done on the NTP page –> Symmetric Keys –> Auto-Generate Keys:
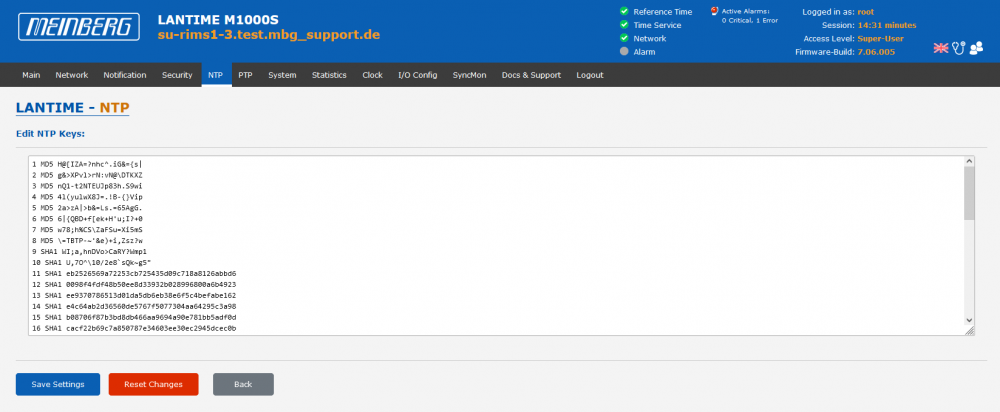
2. Newly generated keys are appended to the key file. The key file can be reviewed on the NTP page –> Symmetric Keys –> Edit NTP Keys:
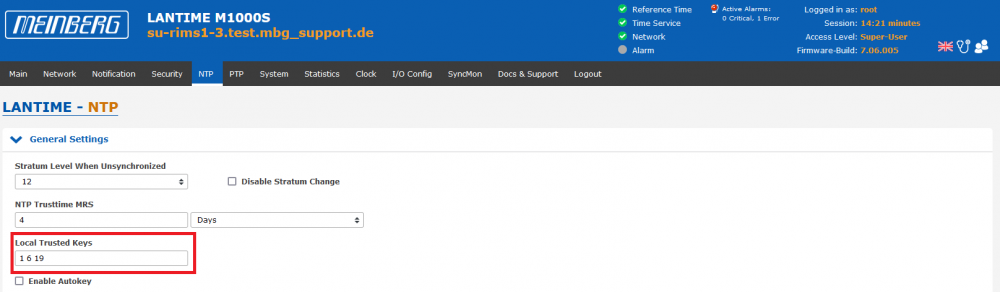
3. Keys have to be defined as trusted keys on the NTP page –> General Settings –> Local Trusted Keys:
In the example above the keys with ID 1, 6 and 19 were defined as trusted keys. The key ID can be found in the first column of the key file. If the LANTIME shall support more than 1 key, the IDs have to be separated by a blank in the Local Trusted Keys field (as in the example above). Keys which are not defined as trusted key cannot be used by a NTP client for symmetric key authentication.
Configure the LANTIME to ignore all NTP packets that are not cryptographically authenticated
As mentioned initially, even if the LANTIME is prepared for symmetric key authentication, NTP clients which request the LANTIME without a key are still getting served with time. If you want the LANTIME to ignore all NTP packets that are not cryptographically authenticated, you have to add the notrust keyword to the default ntpd restrictions. The notrust option tells ntpd to ignore all packets which are not crytographically authenticated. DO NOT use notrust unless symmetric keys has been properly configured. Here the procedure how to add notrust:
1. Connect with a super user account via SSH to the command line interface
2. Open the additional ntp configuration file with the nano editor. The command is nano /etc/ntpconf.add
3. Add the following 2 lines to the file:
restrict default noquery noepeer notrust restrict -6 default noquery noepeer notrust
4. Press CTRL + O to save and then CTRL + X to close the nano editor
5. Run the command sudo lt_cmd reload_config to apply the changes
6. Run the command sudo saveconfig to save your changes permanently
Configuration Steps on a Linux NTPD Client
1. The key has to be copied to the client's key file. On a Linux ntpd client, the file is usually stored in /etc/ntp.keys. For example, if the ntpd client has to be configured to use the generated key with ID 1, the entire key has to be copied from the LANTIME key file and appended to the /etc/ntp.keys file, for example:
1 MD5 H@[IZA=?nhc^.iG&={s|
2. ntpd's configuration file, usually /etc/ntp.conf, has to be modified as well. Here an excerpt from a configuration file which defines the key with ID 1 as trusted key. An NTP server with IP 192.168.1.250 is configured to be requested with that key:
keys /etc/ntp.keys trustedkey 1 server 192.168.1.250 minpoll 6 maxpoll 6 key 1
More information about NTP authentication can be found in this knowledge base article.
Further Assistance
If further assistance is required, contact Meinberg Technical Support:
https://www.meinbergglobal.com/english/support/tech-support.htm
— Manuel Schäfer manuel.schaefer@meinberg.de, last updated 2024-07-10